Deploy A Sample Application
This guide walks you through deploying the StartMeUp sample application to your Edka cluster. “StartMeUp” is a Go-based SaaS starter kit, packaged as a Helm chart. It serves as a foundational example that you can adapt and extend for your specific requirements.
Important
To get it working, you have to fork the StartMeUp repo and make the necessary changes (e.g., update with your container registry and ingress endpoint) to push the image and helm chart to your own GitHub Container Registry.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”- You have completed the steps in Build Your Own PaaS, which sets up your Edka cluster, PostgreSQL, GitHub integration, Container Registry and Doppler integration.
- You have your GitOps repository (e.g., edkadigital/blueprint) cloned locally.
- StartMeUp is forked to your own GitHub account and configured to push the image and helm chart to your own GitHub Container Registry
- You have access to a Doppler project where you can manage secrets for the application.
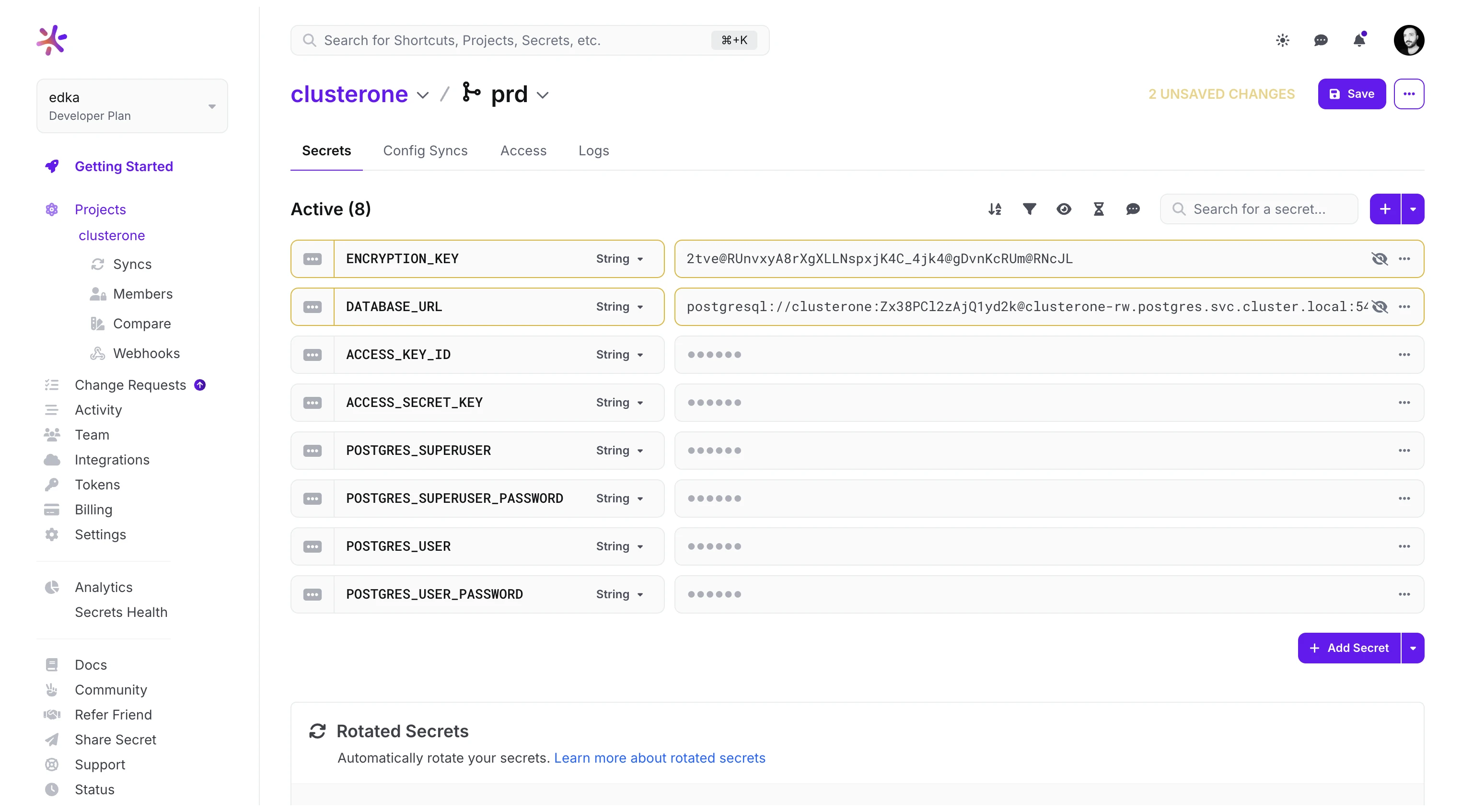
1. Prepare Application Secrets in Doppler
Section titled “1. Prepare Application Secrets in Doppler”The “StartMeUp” application requires two secrets to function correctly:
DATABASE_URL: The connection string for the PostgreSQL database.ENCRYPTION_KEY: A random string used by the application for data encryption.
Create these secrets in your Doppler project associated with this application:
-
DATABASE_URL:postgresql://clusterone:<YOUR_POSTGRES_PASSWORD>@clusterone-rw.postgres.svc.cluster.local:5432/clusterone?sslmode=disableReplace
<YOUR_POSTGRES_PASSWORD>with the actualPOSTGRES_USER_PASSWORDyou configured during the Cloud-Native PostgreSQL setup. -
ENCRYPTION_KEY: Generate a secure, long random string. For example, using OpenSSL:Terminal window openssl rand -hex 32An example key:
a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8i9j0k1l2m3n4o5p6q7r8s9t0u1v2w3x4y5z6
2. Configure GitOps for the Application
Section titled “2. Configure GitOps for the Application”We will add two FluxCD custom resources to your GitOps repository:
- A
HelmReleaseto deploy the application using its private Helm chart. - A
Kustomizationto manage theHelmReleasedependency on other resources, like the External Secrets Operator and PostgreSQL, ensuring they are ready before the application attempts to deploy.
a. Create Application Manifest Directory
Section titled “a. Create Application Manifest Directory”In your local clone of the GitOps repository, create the directory where the application’s manifests will reside:
mkdir -p clusters/resources/clusterone/appb. Define the HelmRelease
Section titled “b. Define the HelmRelease”This resource tells Flux to deploy the “StartMeUp” application using its Helm chart and configure it to automaticaly deploy when the chart is updated.
Create a file named startmeup-helmrelease.yaml in the clusters/resources/clusterone/app/ directory:
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2kind: HelmReleasemetadata: name: startmeup # Name of the HelmRelease object namespace: production # Namespace where the application will be deployedspec: interval: 5m # Reconciliation interval for the HelmRelease chart: spec: chart: startmeup # Name of the Helm chart version: ">=0.0.1" # Use the latest available version (or pin to a specific one) sourceRef: kind: HelmRepository name: edka # Assumes a HelmRepository named 'edka' exists namespace: flux-system # Namespace where the HelmRepository is located interval: 1m # How often to check for new chart versions upgrade: remediation: remediateLastFailure: true # Attempt to fix failed upgrades test: enable: true # Run Helm tests after deployment/upgradec. Define the Kustomization for the Application
Section titled “c. Define the Kustomization for the Application”This Kustomization resource tells Flux to manage the HelmRelease within the clusters/resources/clusterone/app/ directory and respect its dependecies.
Create a file named startmeup-kustomization.yaml in the clusters/clusterone/ directory of your GitOps repository:
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1kind: Kustomizationmetadata: name: startmeup # Unique name for this Kustomization object namespace: flux-system # Namespace where this Kustomization object itself residesspec: dependsOn: # Ensures that the External Secrets Operator and its Doppler integration are ready - name: cluster-secrets-store # Ensures that PostgreSQL is set up and ready before attempting to deploy the app - name: postgres-cluster interval: 5m # How often Flux reconciles this Kustomization retryInterval: 2m timeout: 5m # Max time to wait for all resources to become ready wait: true # Wait for all resources defined in the path to be ready path: "./clusters/resources/clusterone/app" # Path to the application's manifests prune: true # Delete resources removed from the Git repository path sourceRef: kind: GitRepository name: flux-system # Refers to the GitRepository object for your main GitOps repo3. Commit and Push Changes
Section titled “3. Commit and Push Changes”Commit the new manifest files to your GitOps repository and push the changes:
git add clusters/clusterone/startmeup-kustomization.yamlgit add clusters/resources/clusterone/app/startmeup-helmrelease.yamlgit commit -m "Deploy StartMeUp application"git pushFlux will detect these changes and begin the deployment process.
4. Verify Deployment
Section titled “4. Verify Deployment”You can monitor the synchronization and deployment status using Flux CLI commands:
# Verify the status of the Kustomizations in your cluster$ kubectl get kustomizations --all-namespacesNAMESPACE NAME AGE READY STATUSflux-system cluster-secrets-store 143m True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:9b7f9549a89e559efc4e98c743e8703cb52d47d4flux-system flux-system 143m True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:9b7f9549a89e559efc4e98c743e8703cb52d47d4flux-system postgres-cluster 143m True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:9b7f9549a89e559efc4e98c743e8703cb52d47d4flux-system shared-components 143m True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:9b7f9549a89e559efc4e98c743e8703cb52d47d4flux-system startmeup 2m7s True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:9b7f9549a89e559efc4e98c743e8703cb52d47d4# Check the application pods$ kubectl get pods -n production -l app=startmeupNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEstartmeup-684dccb9fc-gm7j4 1/1 Running 0 2m34sstartmeup-684dccb9fc-vg8g5 1/1 Running 0 2m34s# Check the application ingress and access it$ kubectl get ing -n productionNAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGEgo.startmeup.dev nginx go.startmeup.dev 7d4bd02c-7f89-4898-a8da-8f6e69fc525d.fsn1.customers.edka.net 80, 443 4m13sYou can now access the application at the domain you configured in the Ingress resource.