Build Your Own PaaS
Transform your Kubernetes cluster into a full-fledged PaaS with Edka.
This guide demonstrates how to configure a selection of add-ons to enhance your Edka cluster. You can choose to install any add-ons according to your needs, either through the Edka dashboard, GitOps, or directly via the Kubernetes cluster API.
For this example, we’ll cover:
- Installing essential add-ons (ingress, certificates, database operator, secrets management).
- Configuring these add-ons.
- Integrating with external services like a secrets provider, GitHub account and a container registry.
- Enabling GitOps for continuous reconciliation.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”- An Edka cluster (previously created). If you didn’t create one yet, see our Create Your First Cluster guide.
- One or more domain names that you own and can configure DNS records to point to your cluster ingress endpoint.
1. Install Add-Ons
Section titled “1. Install Add-Ons”Start by navigating to Settings in your cluster overview, then go to the Add-ons section.
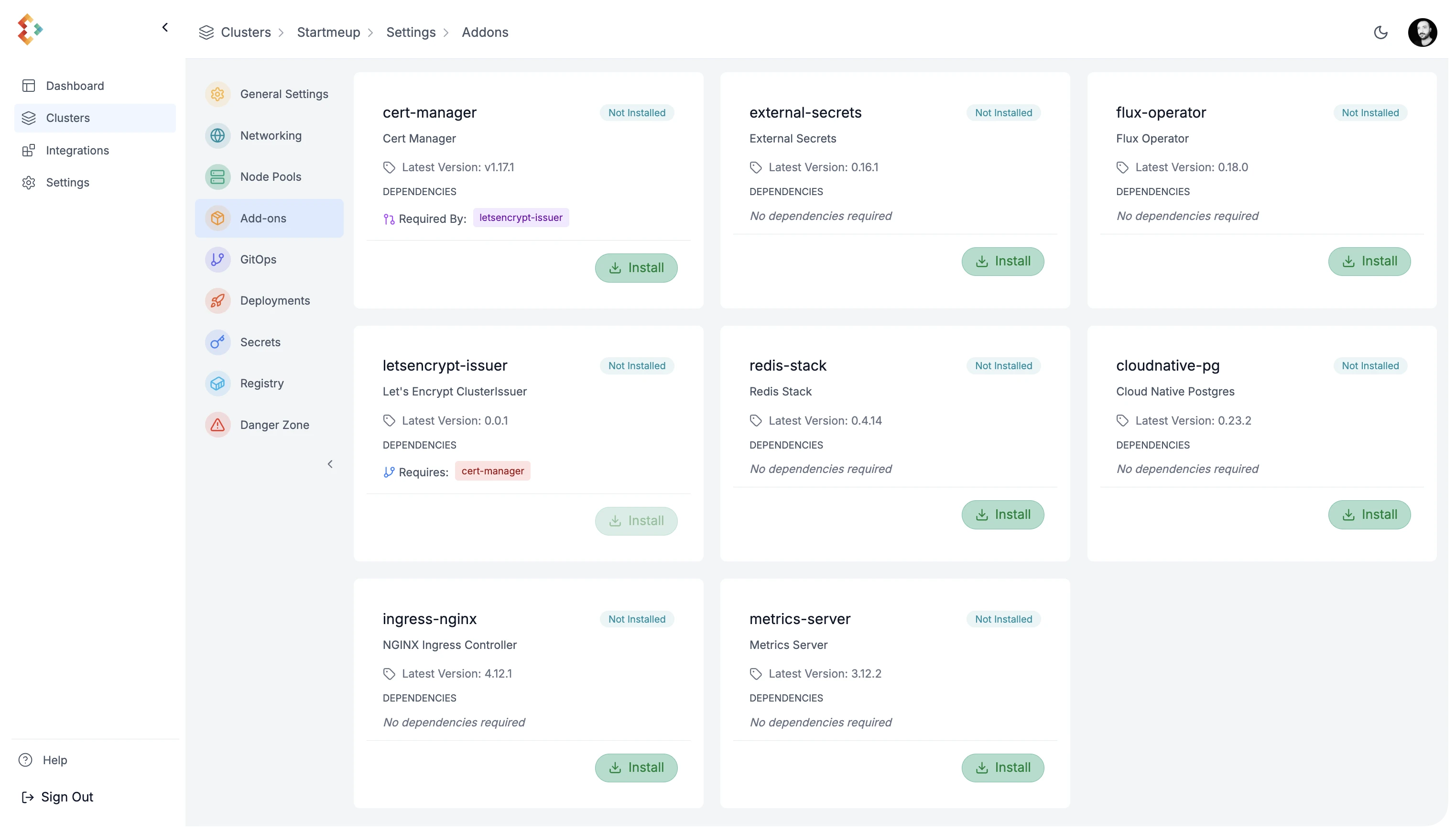
Edka provides a curated set of production ready add-ons that can be installed on your cluster. For this guide, install the following:
- Ingress Controller
An Ingress controller is required to expose your applications to the internet.
It automatically provisions a load balancer from your cloud provider and configures the necessary rules to route traffic to your applications.
- Certificate Management
It integrates with your Ingress Controller to automatically provision and renew TLS certificates for your applications.
- Certificate Issuer
This is required to communicate with the provider for your certificates, in this example Let’s Encrypt, but you can configure other issuers directly on your Kubernetes cluster. Cert Manager add-on is required for this to work.
- Cloud Native Postgres
This is a PostgreSQL operator that automates the provisioning and management of PostgreSQL clusters on Kubernetes. It covers the full lifecycle of a highly available PostgreSQL database cluster with a primary/standby architecture, using native streaming replication.
- External Secrets
This add-on allows you to sync secrets from external providers into your Kubernetes cluster. It supports a wide range of providers, including AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, Doppler, and more.
2. Customize Your Add-Ons
Section titled “2. Customize Your Add-Ons”Some add-ons require additional configuration. While we are working to automate this, some manual steps are currently needed.
Ingress Controller
Section titled “Ingress Controller”Point one or more domain/subdomain DNS records to your cluster’s ingress endpoint. You can find this endpoint in the cluster overview, under Ingress Endpoints.
External Secrets
Section titled “External Secrets”To allow your cluster to fetch secrets from an external provider (this example uses Doppler), create a secret in your cluster with the provider’s credentials. This can be done through the Edka dashboard and referenced in GitOps later.
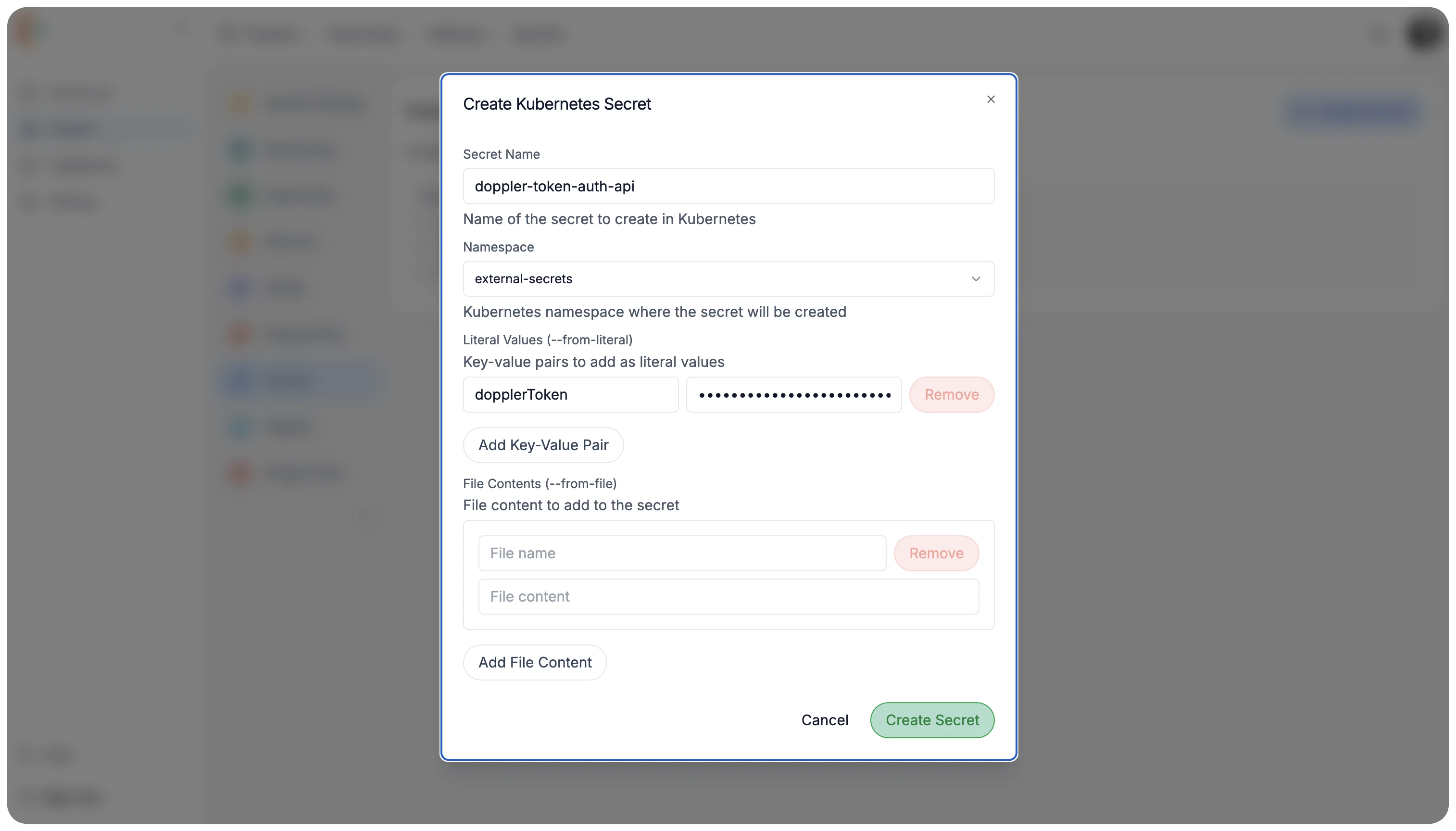
In your cluster’s Settings, navigate to Secrets and create a new secret with the following values:
- Name: doppler-token-auth-api
- Namespace: external-secrets
- Key: dopplerToken
- Value your-doppler-token
Press Create Secret to save the secret.
 The ClusterSecretsStore will use this secret to authenticate with Doppler and fetch secrets for your projects.
The ClusterSecretsStore will use this secret to authenticate with Doppler and fetch secrets for your projects.
In the blueprint repository, edkadigital/blueprint you can find the configuration for the secrets store. You can also create your own secrets store configuration and reference it in your GitOps repository.
Cloud Native Postgres
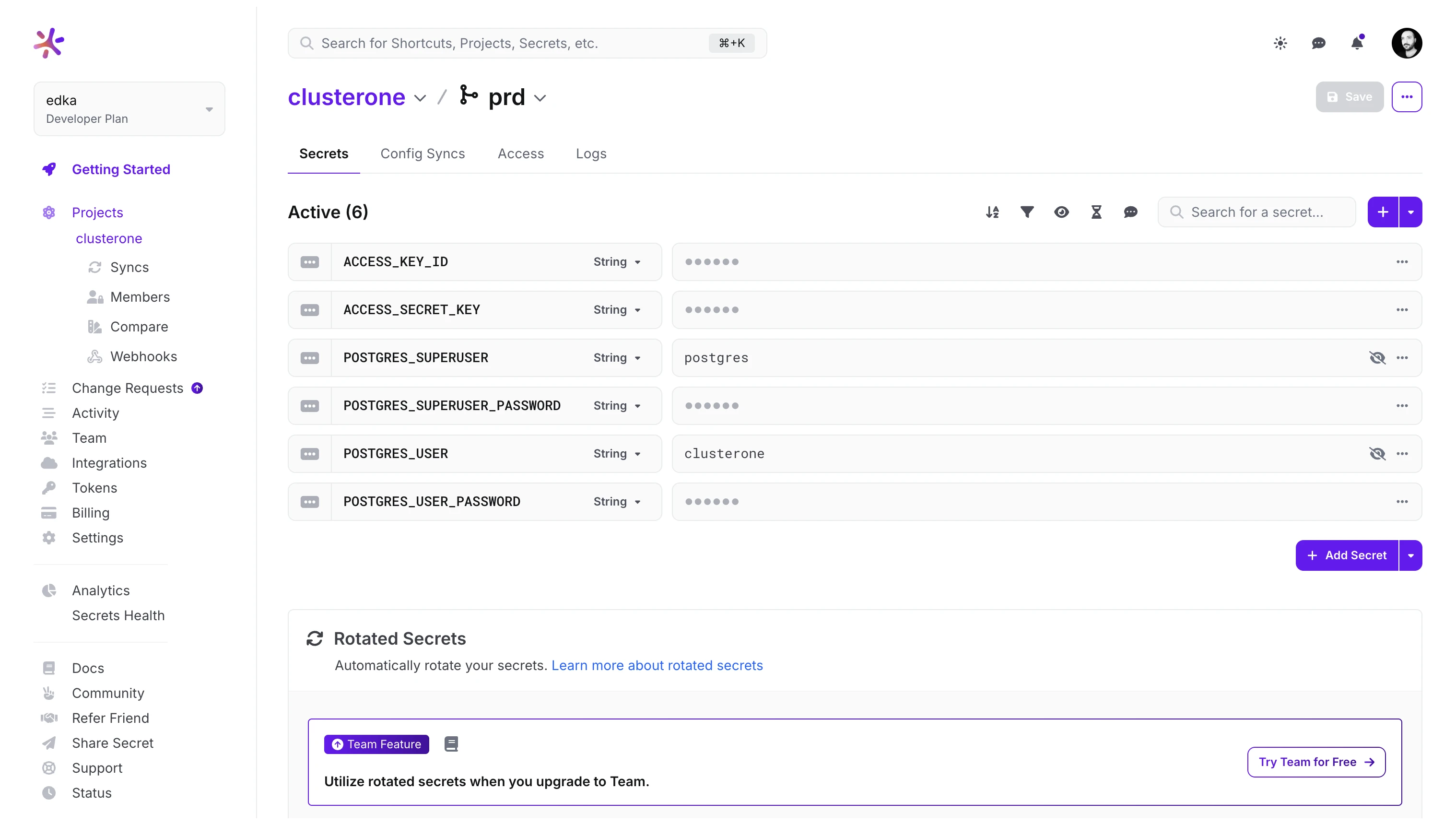
Section titled “Cloud Native Postgres”This add-on requires several credentials for your PostgreSQL database cluster. The blueprint repository is configured to fetch secrets with the following names from Doppler. You will need to create these in your Doppler project:
- Bootstrap Database Credentials:
POSTGRES_USERPOSTGRES_USER_PASSWORD
- Cluster SuperUser Credentials:
POSTGRES_SUPERUSERPOSTGRES_SUPERUSER_PASSWORD
- AWS S3 Credentials (for database backups):
ACCESS_KEY_IDACCESS_SECRET_KEY
The blueprint repository is configured to automatically use these Doppler secrets to create the necessary Kubernetes secrets in your cluster.
3. Enable GitOps
Section titled “3. Enable GitOps”Enable continuous reconciliation for your applications and cluster resources. Our initial release supports GitHub repositories, with other providers planned for future updates.
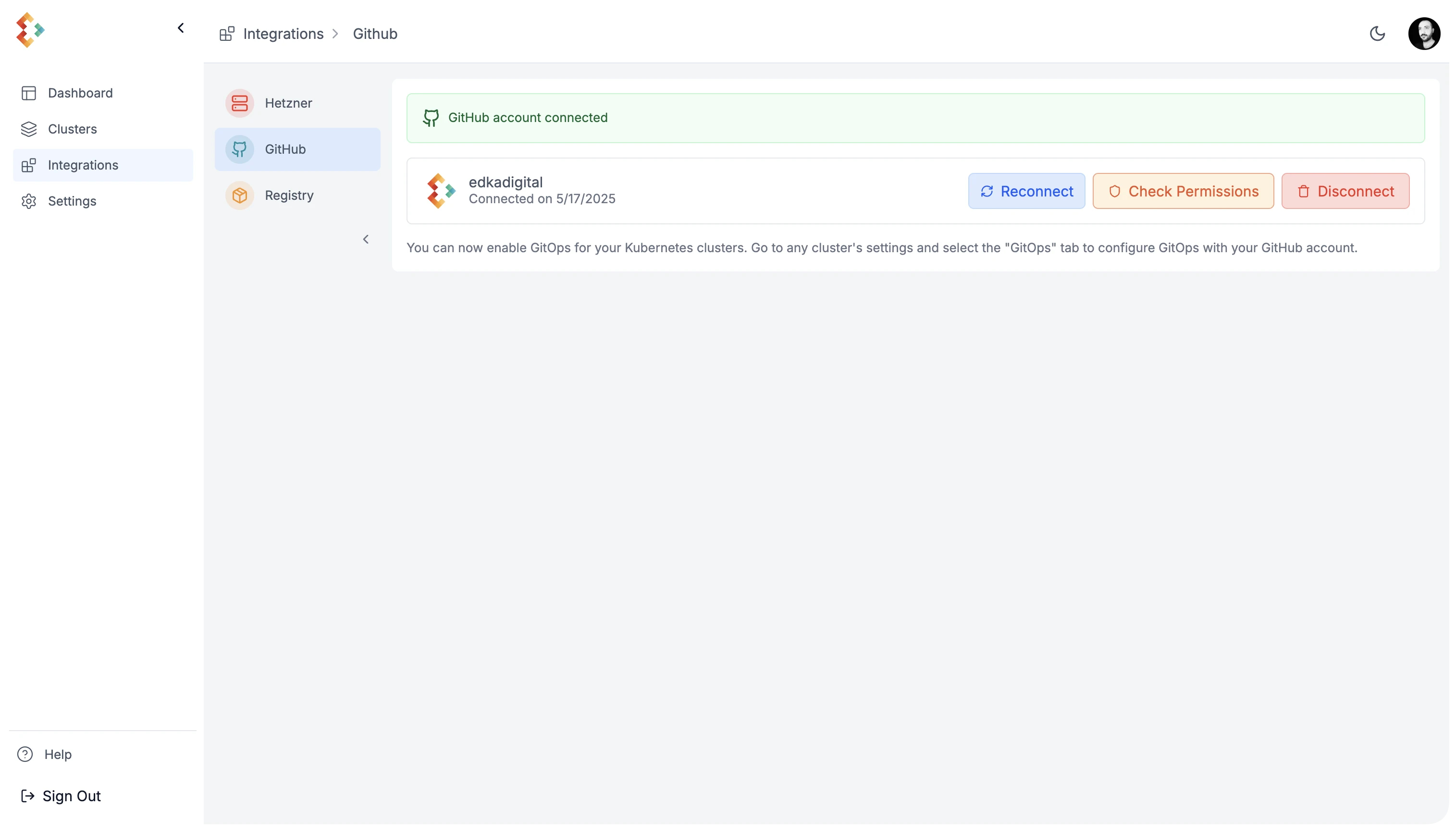
GitHub Integration
Section titled “GitHub Integration”First, integrate with GitHub by navigating to Settings > Integrations > GitHub. Grant permissions to the repositories you plan to use.
GitOps Configuration
Section titled “GitOps Configuration”Once permissions are granted, go to your cluster’s Settings > GitOps. Select the repository and branch for GitOps.
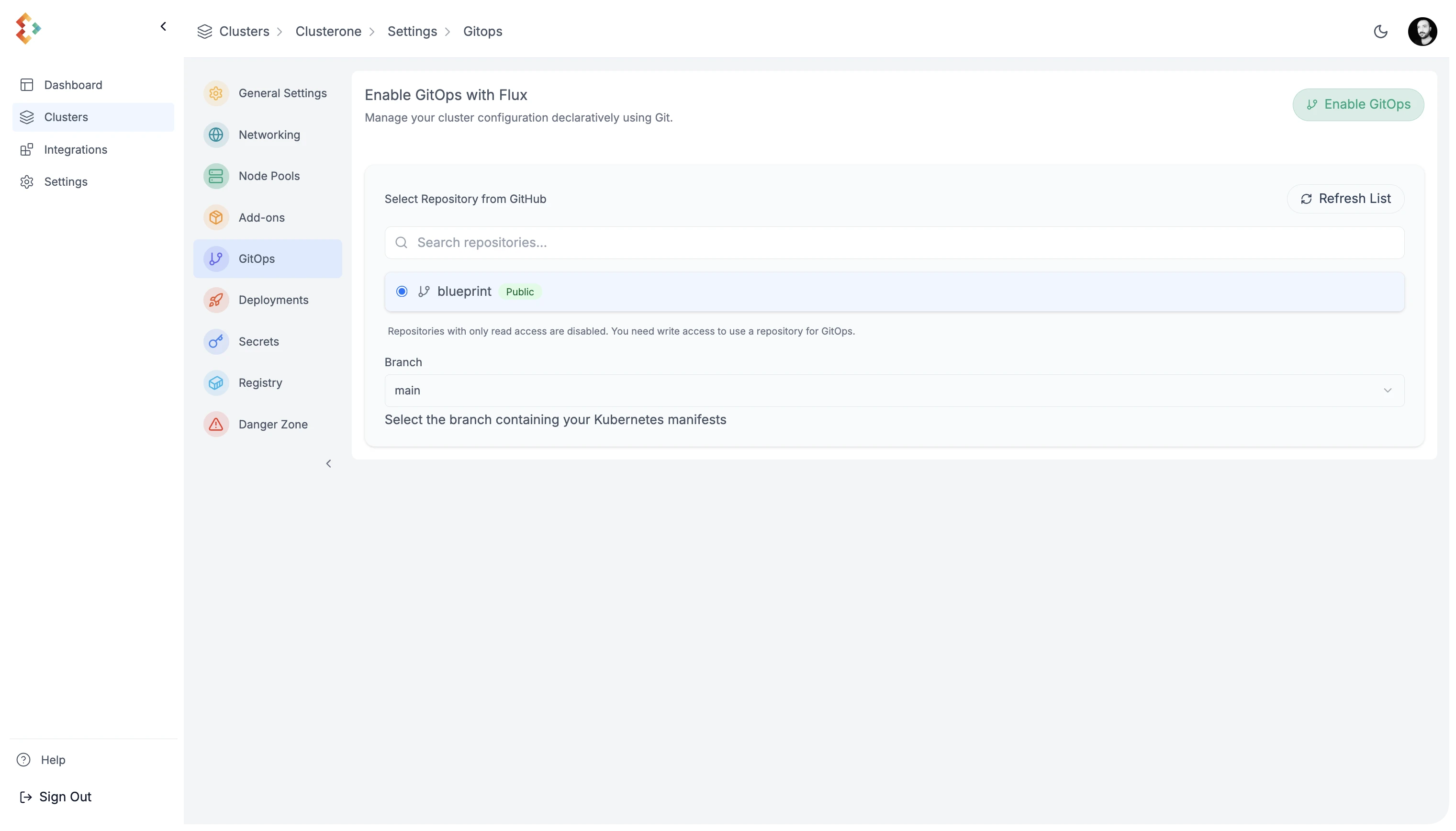
In this example we connect edkadigital/blueprint repository to the cluster, which provides a blueprint for the cluster and add-ons configuration. You can inspect the GitOps reconciliation status in the cluster, using kubectl command line tool or Lens IDE.
$ kubectl get kustomizations --all-namespacesNAMESPACE NAME AGE READY STATUSflux-system cluster-secrets-store 9m23s True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:c97b810d9d8d0ffc5f70c80a23fe252e7bf13bc7flux-system flux-system 9m29s True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:c97b810d9d8d0ffc5f70c80a23fe252e7bf13bc7flux-system postgres-cluster 9m23s True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:c97b810d9d8d0ffc5f70c80a23fe252e7bf13bc7flux-system shared-components 9m23s True Applied revision: refs/heads/main@sha1:c97b810d9d8d0ffc5f70c80a23fe252e7bf13bc74. Connect a Container Registry
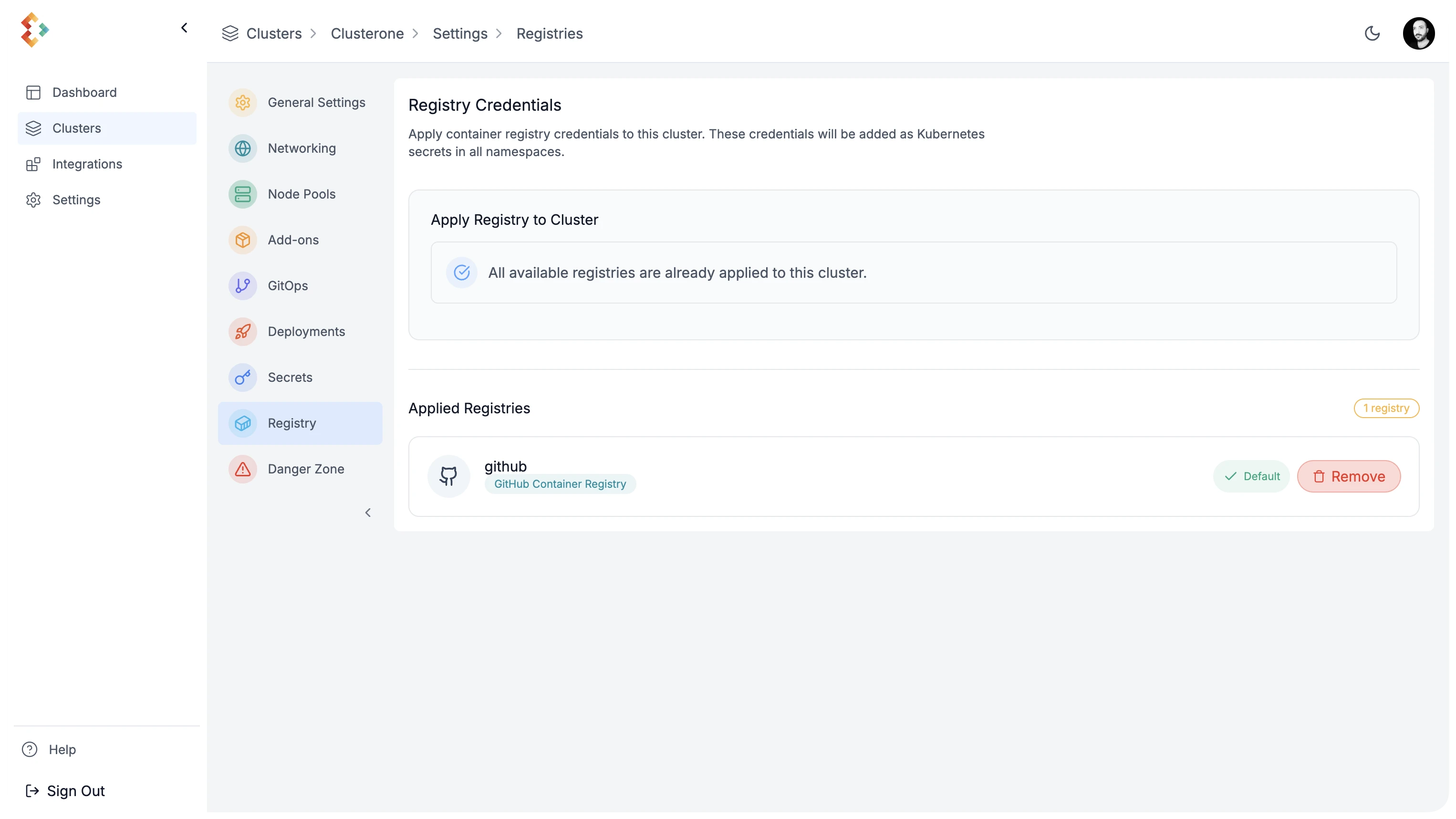
Section titled “4. Connect a Container Registry”Edka supports several container registries, including GitHub Container Registry, Docker Hub, AWS ECR, and Google Artifact Registry. This example uses GitHub Container Registry.
Navigate to Settings > Integrations > Registry and select your container registry. Follow the specific instructions for your chosen registry to connect it to your cluster.
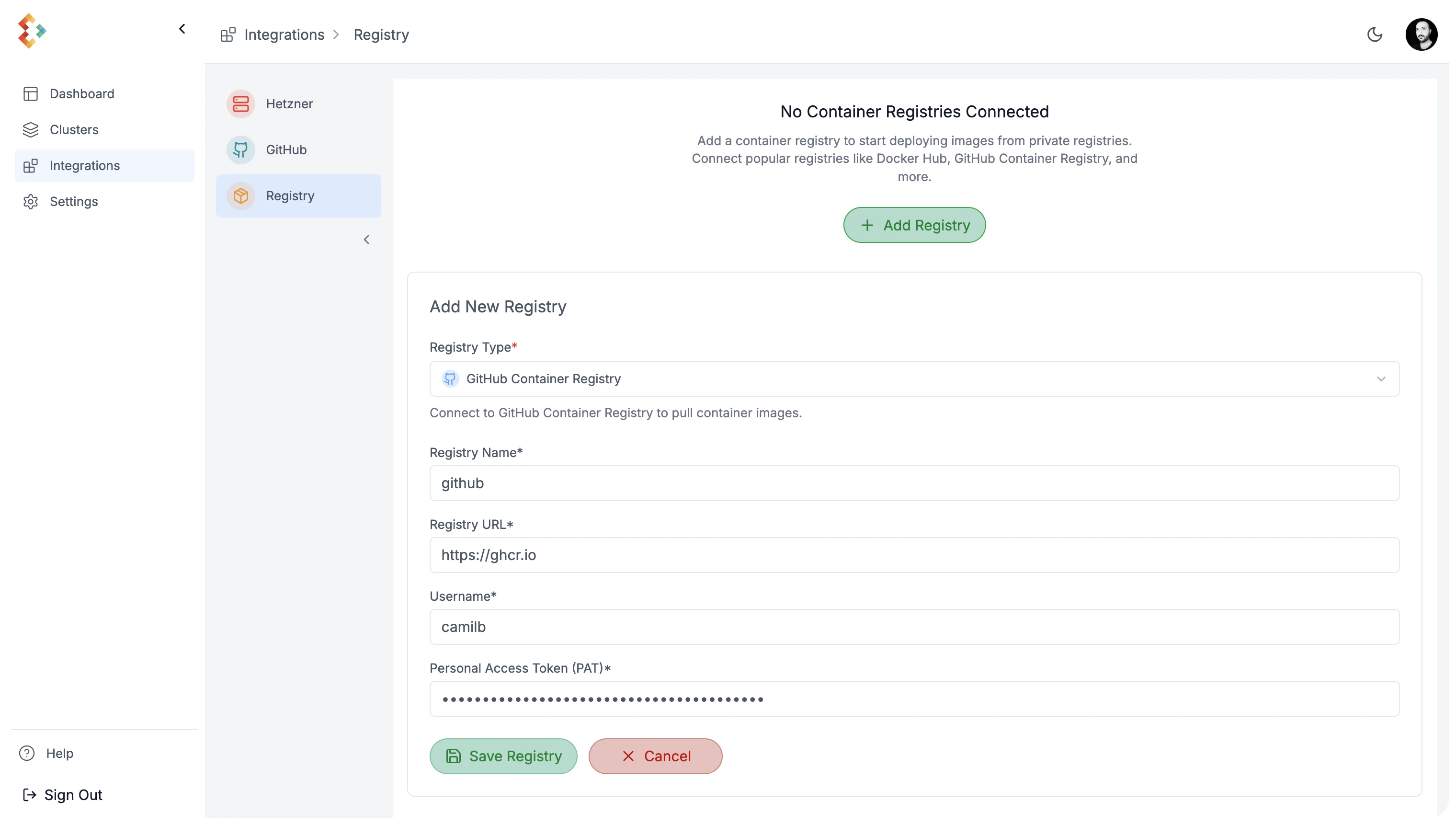
Once connected, you have to enable this registry to your cluster and set it as the default registry for your workloads.
This can be done in the cluster Settings > Registry > Apply Registry > Set as Default.